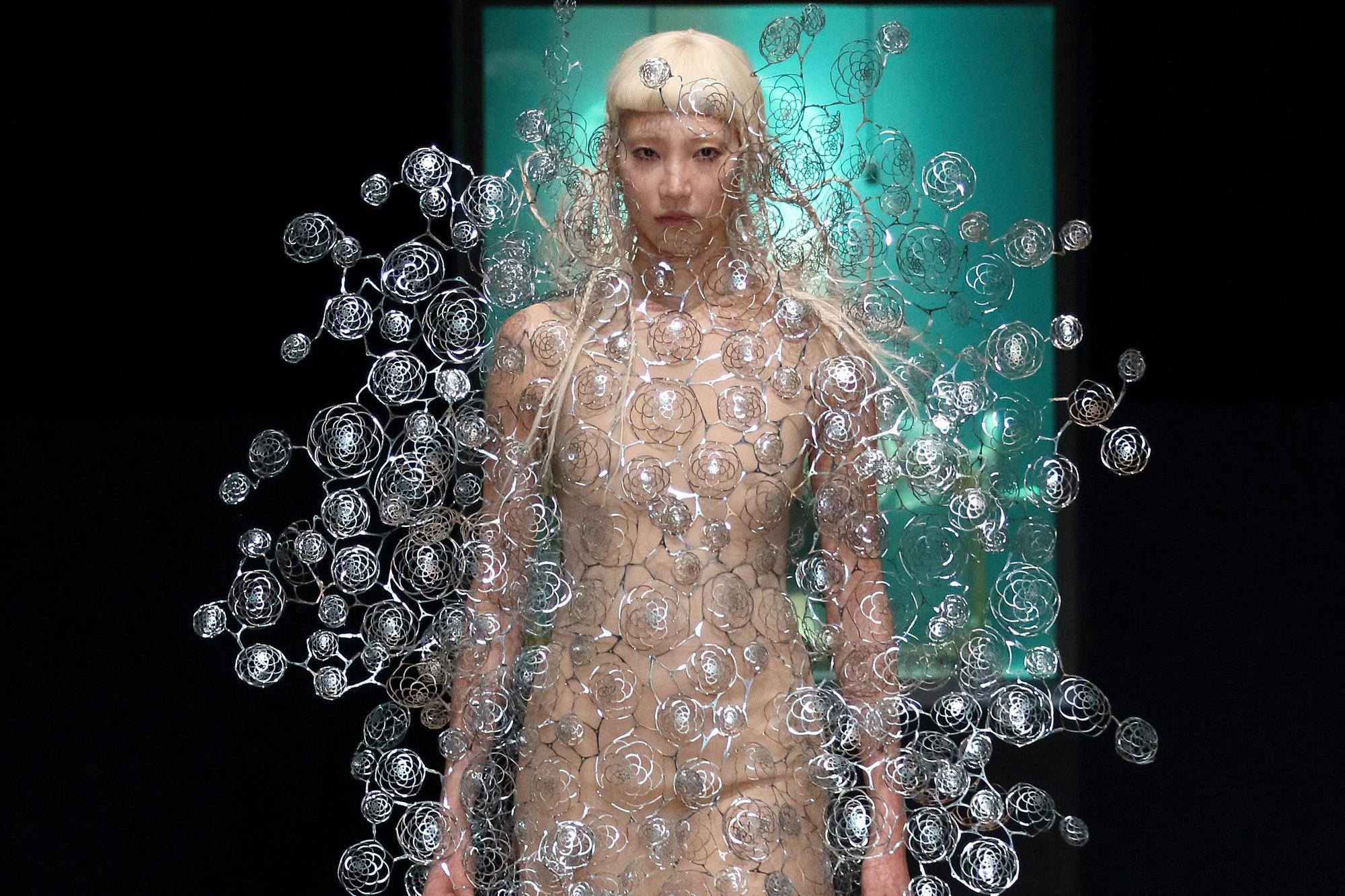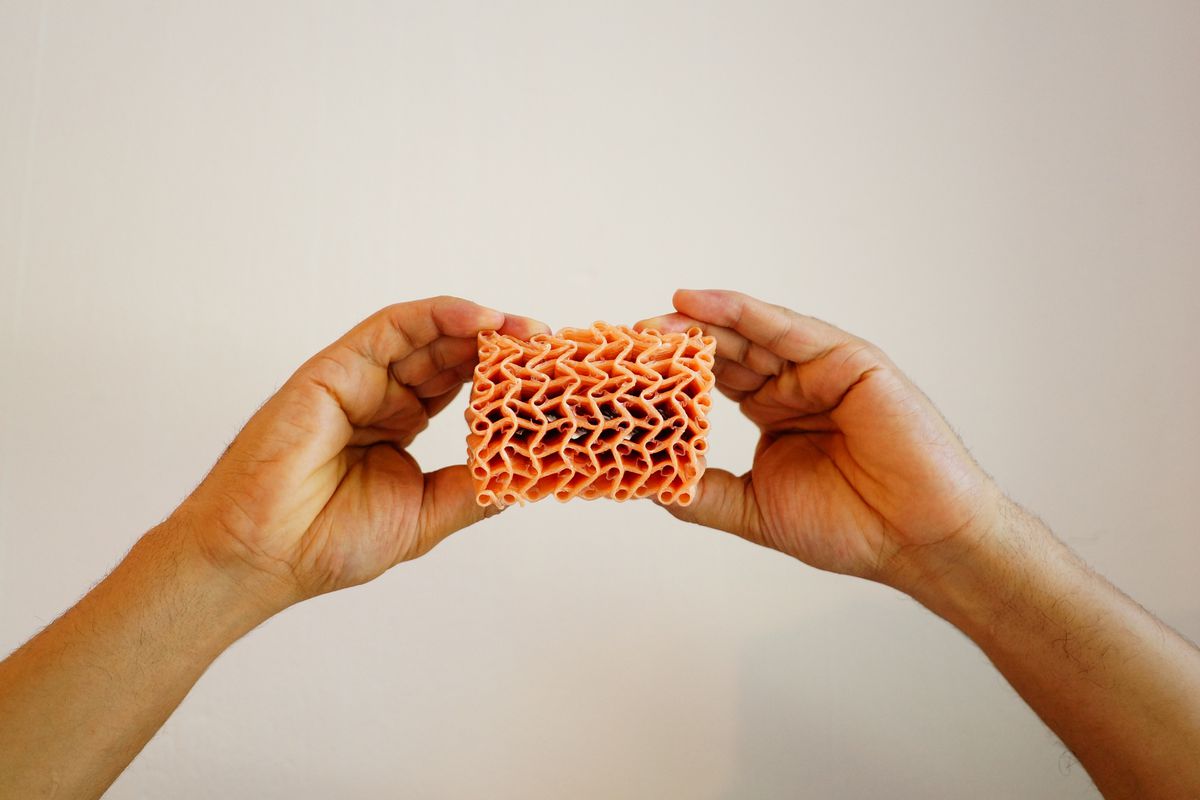
The textile industry is constantly evolving, and one of the most exciting new developments is 3D weaving. This innovative technology allows for the creation of seamless, three-dimensional garments and fabrics with intricate designs and complex shapes, directly on the loom.
Making a mark with innovations and applications
Unlike traditional weaving, which produces flat fabric, 3D weaving interlaces yarns in three perpendicular directions (x, y, and z) to create complex shapes and structures within the fabric itself. This opens up a world of possibilities for both aesthetics and functionality.
While both 3D weaving and seamless/whole garment knitting produce seamless garments, they differ in their underlying technology and end applications. 3D weaving interlaces yarns in three dimensions to create woven fabrics with complex structures and thicknesses. It’s ideal for tailored garments, technical textiles, and applications requiring high strength and durability. Seamless/whole garment knitting on the other hand uses knitting needles to create complete garments with minimal seams. It is well-suited for sportswear, knitwear, and applications prioritizing flexibility and comfort.
The advantages of 3D weaving are many. Most importantly, it minimizes fabric waste by creating near-net-shape products. The seamless garments that are made with this technology offer superior comfort and fit. 3D woven fabrics can provide improved breathability, moisture management, and support. Also it can help create complex shapes and intricate patterns that directly on the loom.
Innovations
Multi-layer fabrics: 3D weaving can produce fabrics with multiple layers, each with different properties or materials. This allows the creation of garments with integrated functions, such as moisture-wicking inner layers and abrasion-resistant outer layers.
Complex shapes: 3D weaving creates seamless, three-dimensional shapes directly on the loom, reducing the need for cutting and sewing. This is particularly useful for producing complex components like shoe uppers, contoured cushions, and even medical implants.
Integrated functionality: This technology can integrate functional elements directly into the fabric, such as sensors, actuators, and electronic components. This has applications in areas like smart textiles, wearable technology, and medical devices.
Applications
3D weaving is seeing numerous applications. In fashion, it leads to seamless garments, complex shapes, and intricate textures for high-end fashion and sportswear. In technical textiles it creates lightweight and strong composites for aerospace, automotive, and construction industries. In medical space, it helps in producing implants, prosthetics, and customized support structures with biocompatible materials. The technology is being used to produce sports equipment like helmets, protective gear, and footwear with enhanced performance and comfort.
Indeed, 3D weaving also has certain limitations. One major one is cost as 3D weaving technology is currently more expensive than traditional weaving. Production speed is another bane as 3D weaving can be slower than traditional methods, especially for complex designs. Limited material selection is also an issue as not all yarns are suitable for 3D weaving. What’s more designing 3D woven fabrics requires specialized skills and software.
While 3D weaving can create near-net-shape garments, it's not always a completely "yarn to apparel" process. Some finishing steps, such as minor trimming or the addition of closures, might be required. However, it significantly reduces the reliance on traditional cut-and-sew methods, streamlining production and minimizing waste. But the fact is, 3D weaving has the potential to reduce excess clothing in several ways. First, it helps in on-demand manufacturing which means producing garments only when needed that minimizes overstocking and waste. It also helps in customization and encourages consumers to invest in longer-lasting, personalized garments instead of disposable fashion. The seamless construction and high-performance materials increase garment lifespan. And 3D woven fabrics from recyclable materials can be more easily repurposed or broken down for reuse.
Startips, brands show the way
Many startups and brands are exploring the potential of 3D weaving. For example, Ministry of Supply, uses 3D knitting technology to create seamless, responsive apparel. Similarly, Unspun develops custom-fit jeans using 3D weaving technology. Twine Solutions offers innovative 3D weaving solutions for technical textiles and composites.
While still in its early stages of adoption, some apparel brands are incorporating 3D weaving into their production. Adidas for example utilized 3D knitting for its Future craft footwear line. And Nike employed Flyknit technology (a form of 3D knitting) in various footwear and apparel products.
Indeed 3D weaving is a promising technology with the potential to transform various industries, including fashion. While challenges remain in terms of cost and scalability, ongoing innovations and increasing adoption suggest a bright future in textile and apparel sector. As R&S continue, more creative and impactful applications of 3D weaving are expected to emerge in future.












